Java 디자인 패턴-02.Factory Method
(Java 디자인 패턴 스터디 모집 중 : https://github.com/bluedskim/javaDesignPatterns)
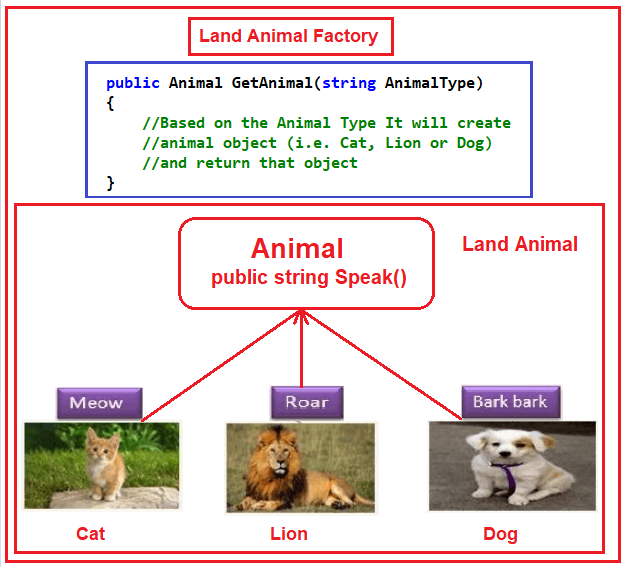
(출처:Abstract Factory Design Pattern in C#)
해결하려는 문제
- 생성자를 직접 호출해서 객체를 생성하는 경우 해당 객체와 클라이언트가 강하게 결합되게 되어 확정성이 떨어진다.
개요
- 생성자를 호출하지 않고 생성하기 위한 패턴(생성될 클래스를 지정하지 않는다)
- 해당 클래스를 사용하는 클래스에 하드코딩을 없앨 수 있다.
클래스 다이어그램
소스
- Shape.java : 도형(인터페이스)
1 2 3 4 5package net.dskim.desingpattern.factorymethod; public interface Shape { String draw(); } - 도형 객체들 : Shape.java 를 implement
- Rectangle.java : 사각형
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8package net.dskim.desingpattern.factorymethod; public class Rectangle implements Shape { @Override public String draw() { return "draw Rectangle"; } } - Circle.java : 원
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8package net.dskim.desingpattern.factorymethod; public class Circle implements Shape { @Override public String draw() { return "draw Circle"; } } - Square.java : 정사각형
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8package net.dskim.desingpattern.factorymethod; public class Square implements Shape { @Override public String draw() { return "draw Square"; } }
- Rectangle.java : 사각형
- ShapeFactory.java : 도형 팩토리(Virtual Constructor)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21package net.dskim.desingpattern.factorymethod; public class ShapeFactory { // use getShape method to get object of type shape public Shape getShape(String shapeType) { if (shapeType == null) { return null; } if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")) { return new Circle(); } else if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")) { return new Rectangle(); } else if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")) { return new Square(); } return null; } } - 클라이언트 : FactoryMethodTest.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37package net.dskim.desingpattern.factorymethod; import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; @Slf4j public class FactoryMethodTest { @Test public void decoratorTest() { ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory(); // get an object of Circle and call its draw method. Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE"); // call draw method of Circle String drawResult = shape1.draw(); log.info("className={}, drawResult={}", shape1.getClass().getSimpleName(), drawResult); assertEquals("draw Circle", drawResult); // get an object of Rectangle and call its draw method. Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE"); // call draw method of Rectangle drawResult = shape2.draw(); log.info("className={}, drawResult={}", shape2.getClass().getSimpleName(), drawResult); assertEquals("draw Rectangle", drawResult); // get an object of Square and call its draw method. Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE"); // call draw method of square drawResult = shape3.draw(); log.info("className={}, drawResult={}", shape3.getClass().getSimpleName(), drawResult); assertEquals("draw Square", drawResult); } }